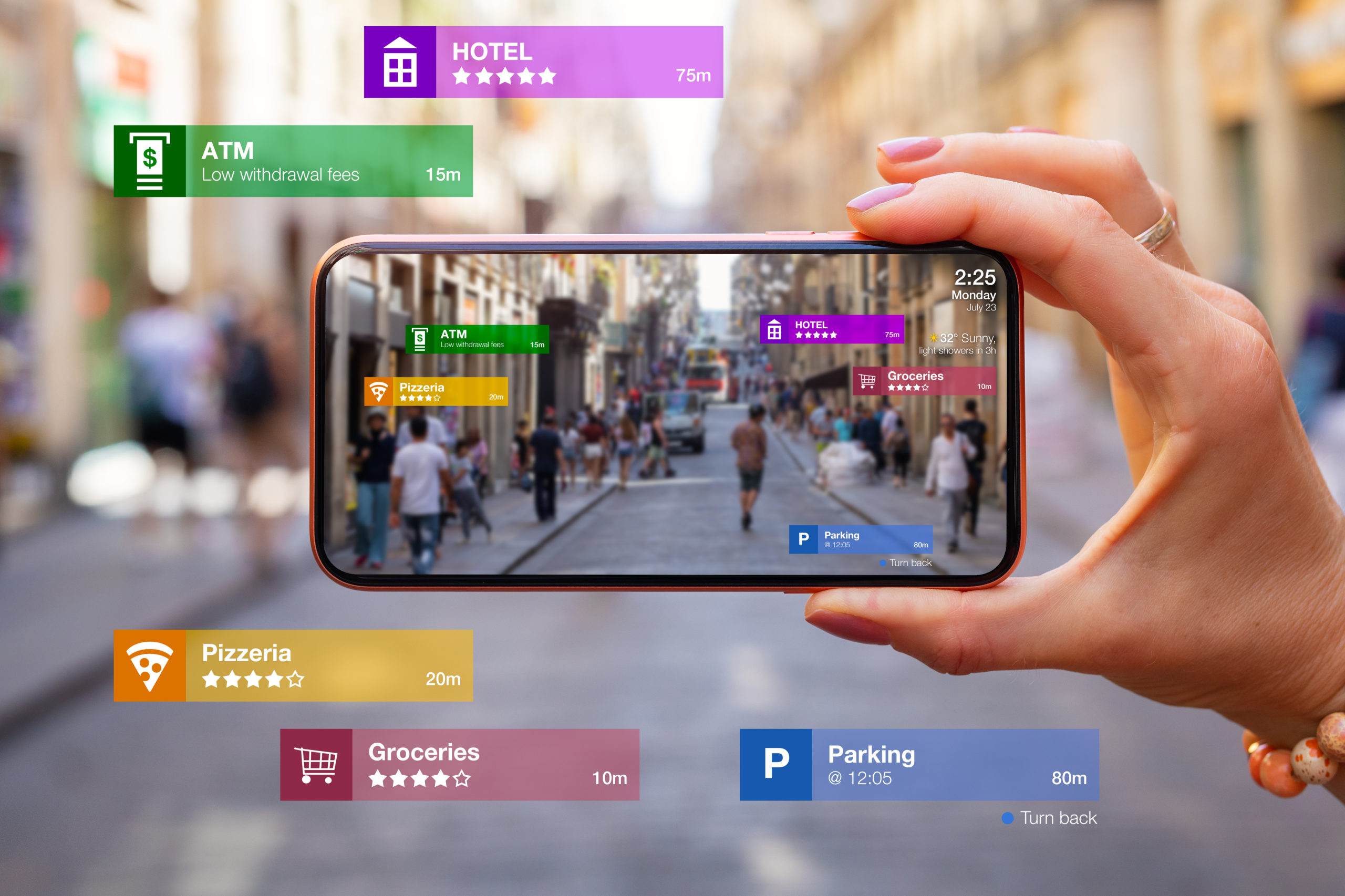
Augmented and Virtual Reality experiences are reshaping the way potential customers interact with products. We believe that the XR product marketing space will continue to grow for years to come.
Location Based AR is an Augmented Reality experience where its context is tied to its use at a specific location. There are endless possibilities for connecting AR to the physical world.
Many developers, including Niantic and Snapchat, are creating Location Based AR experiences that tie cyberspace and the real world closer and closer together.
Niantic Lightship
Niantic is the developer behind Pokemon GO, the app that brought AR into the mainstream in 2016. They’ve used their learnings from multiple AR applications to create Lightship, a platform for third-party developers like Fishermen to develop their own Location Based AR experiences.
Lightship’s core technologies include:
- Real-time Mapping to enable physics for virtual objects.
- Semantic Segmentation to distinguish between different surface types (eg, ground vs sky).
- Robust Multiplayer to create a synchronized, networked, shared experience.
- Virtual Positioning System (Later in 2022) to enable persistent experiences tied to geographic locations.
Let’s take a look at some of Niantic’s Lightship projects.
PGA
Developers used Lightship to design an AR golf game for the Professional Golf Association (PGA). This app allows users to virtually play golf in a real landscape using colorful cartoon characters.

Coachella
Coachella wanted to use their butterfly symbol for a flashy new promotional campaign. Using Lightship, developers added a feature to the Coachella app that allows users to view a giant virtual butterfly landing on the Coachella’s Spectra tower.
Pokemon GO
In Pokemon GO, players can physically travel to locations to earn rewards by interacting with digital markers located at real-world locations. This creates a real-life version of the gameplay in traditional, non-AR Pokemon games.
The success of Pokemon GO can hardly be overstated. According to Statista, in-app purchase revenues for the game surpassed $904 million worldwide in 2021. Unlike traditional mobile games, Pokemon GO has wide economic effects beyond cyberspace. Businesses can tag their locations (for a price) as in-game waypoints. They can also simulate in-game raids by choosing when pokemon hatch. A florist, for example, could set up a grass-type gym at their shop, enticing people to come in and perhaps buy some flowers.
According to Niantic, the real-world effects are significant:
- 73% of players deviate from regular walking routes to achieve in-game milestones
- 84% of players interacted with real-world locations
- 58% of players made a transaction with those locations
Additionally, Niantic partners with businesses on promotions that blur the lines between game and advertising. Niantic and Circle K have partnered to bring redeemable real-world rewards to Pokemon GO. Players can rack up in-game points to redeem for Circle-K coffee, candy, hot dogs, and drinks. Customer rewards change on a monthly or seasonal basis.

Snapchat Landmark Tracking
Landmarker Tracking tracks the physical features of a landmark at a specific location to create a 3D experience around the landmark’s architecture. For example, one such project creates an AR video of New York’s Flatiron building growing eyes and wobbling.
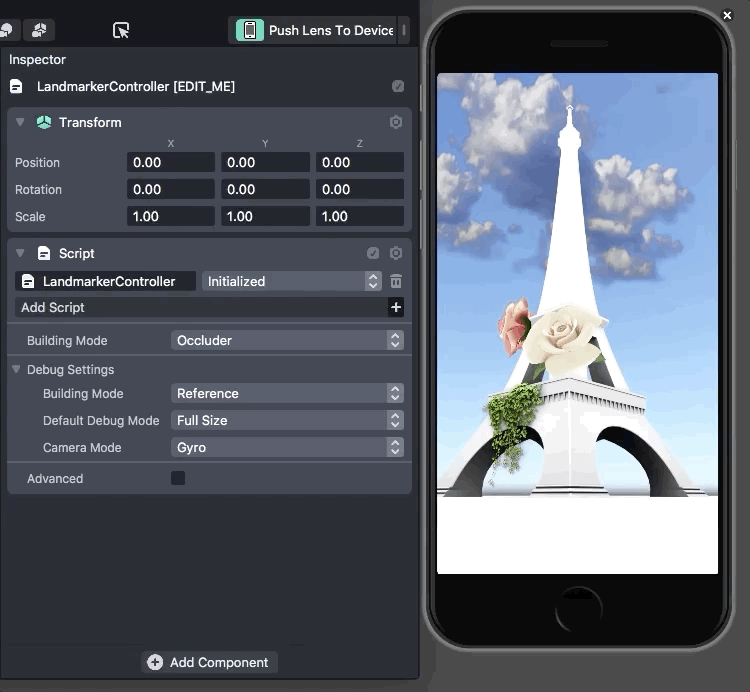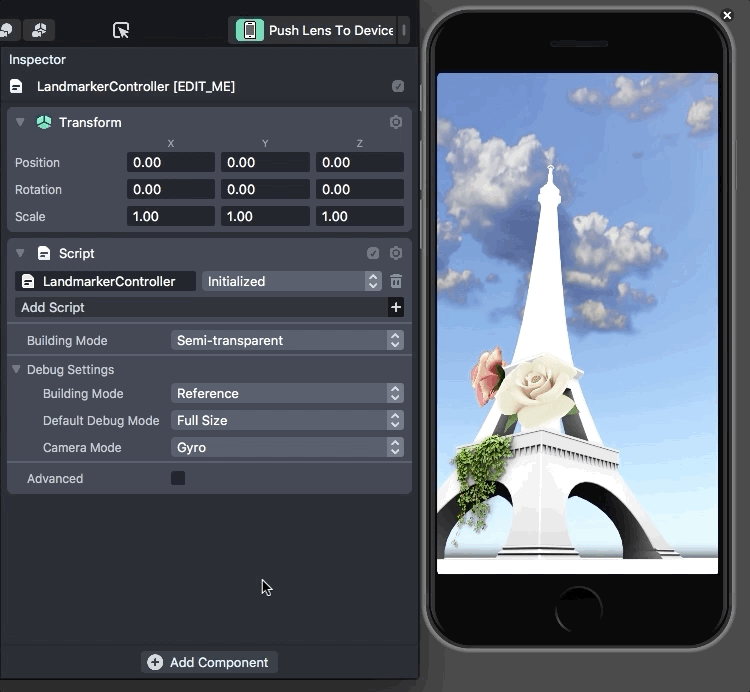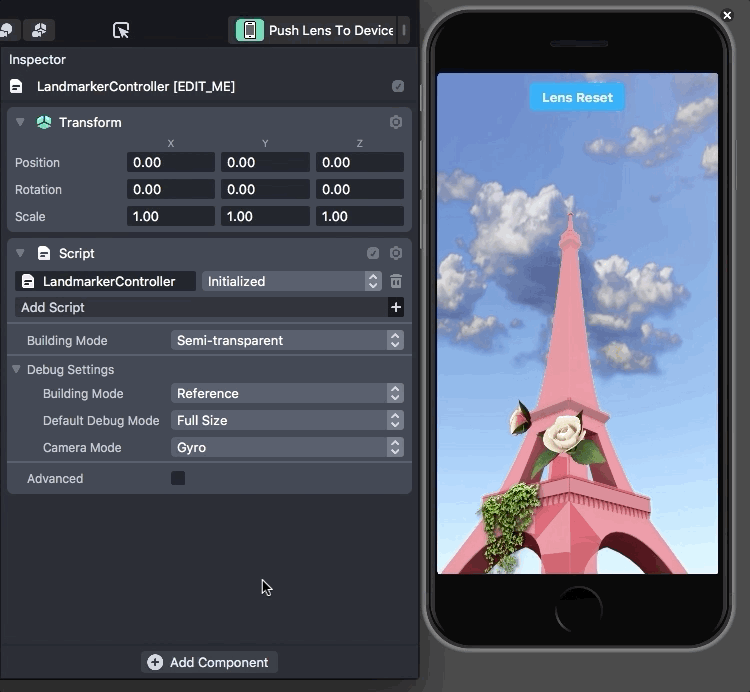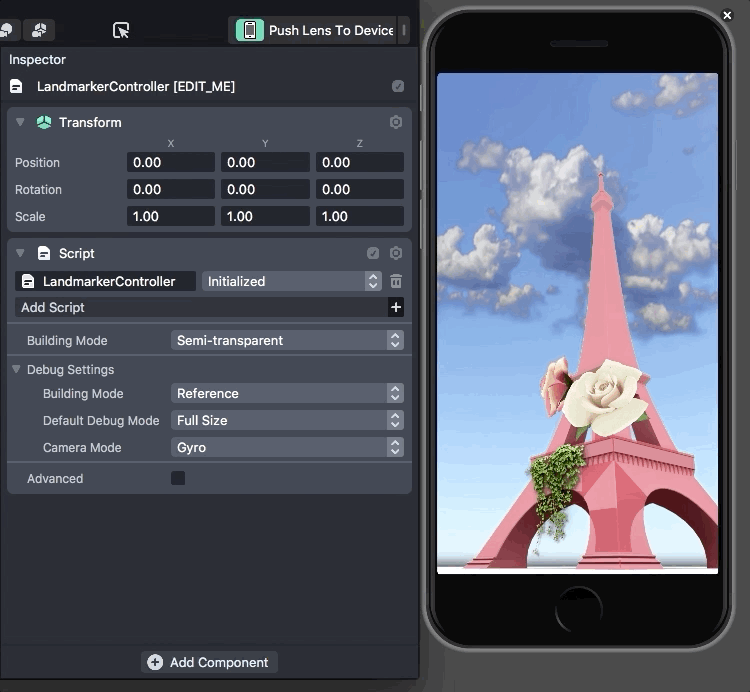
Using LiDAR sensors, developers can scan the outside of real-world locations to create a 3D model. They can then use the 3D model as the basis for an AR experience. Users simply need to face their camera towards the building with the app to see the effect.
Verizon / Snapchat partnership
Verizon partnered with Snapchat to launch a series of Lenses across the US to transform landmarks and artwork into AR experiences.
For their first partnership, they transformed the NY Public Library into a “next generation stage”, where users can watch the library explode with flora, fauna, and a dancing man.

Marker Based AR At Locations

While not as high tech as GPS-based options, marker images can be used to create local AR experiences. Simply place an image down with a QR code or Snap code, then scan. Several companies have used this technique for marketing purposes:
Ally Bank’s Monopoly
In six US cities, Ally placed tiles on the ground that represented the 36 squares of a Monopoly board. Users would scan the square to collect them, and view an AR animation. In all, the campaign received 100,000 plays, suggesting a high degree of engagement.
Lego Store
As far back as 2009, Lego used an AR experience to help customers see finished models before they make a purchase. Lego unveiled an updated experience in 2021 to show a whole scene taking place inside an in-store display case.
Future Possibilites
Developers have barely begun to map the vast field of possibilities that Location Based AR can bring. Some ideas include:
- “Coloring in” statues and artworks
- Animating museum diorama models
- AR murals
- Scavenger hunt games
We believe that, as technology improves, location based AR will become a widespread and mainstream technology. Our work at Fishermen Labs assists companies in creating bespoke AR experiences, many of which are location based experiences.